 Nginx (произносится как "двигатель х") является свободным, открытым исходным кодом, высокопроизводительного HTTP-сервер. Nginx известен своей стабильностью, богатым набором функций, простой настройкой и низким потреблением ресурсов. В этом учебнике показано, как можно установить Nginx на CentOS 6.0 сервер с поддержкой PHP5 (через FastCGI) и MySQL поддержкой. На данный урок имеется виртуальный образ готового сервера, ознакомиться с которым подробней и скачать его можно на форуме Nginx в CentOS 6.0 + скачать.
Nginx (произносится как "двигатель х") является свободным, открытым исходным кодом, высокопроизводительного HTTP-сервер. Nginx известен своей стабильностью, богатым набором функций, простой настройкой и низким потреблением ресурсов. В этом учебнике показано, как можно установить Nginx на CentOS 6.0 сервер с поддержкой PHP5 (через FastCGI) и MySQL поддержкой. На данный урок имеется виртуальный образ готового сервера, ознакомиться с которым подробней и скачать его можно на форуме Nginx в CentOS 6.0 + скачать.
Предварительные замечания
В данной статье я использую имя хоста server1.example.com с IP адресом 192.168.1.101. Эти параметры могут отличаться в Вашем случае, поэтому Вам придется заменить их в случае необходимости.
Включение дополнительных репозиториев
php-fpm не получится получить из официальных репозиториев CentOS, но с Remi RPM репозиториями, которая сама зависит от EPEL хранилищ, мы можем включить их следующим образом:
|
Изменим /etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo ...
|
... и добавьте строку priority=10 в [epel] раздел:
[epel]
name=Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux 6 - $basearch
#baseurl=http://download.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/6/$basearch
mirrorlist=https://mirrors.fedoraproject.org/metalink?repo=epel-6&arch=$basearch
failovermethod=priority
enabled=1
priority=10
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-EPEL-6
[...]
Затем то же самое для [remi] раздел в /etc/yum.repos.d/remi.repo, плюс измененим enabled на 1:
|
[remi] name=Les RPM de remi pour Enterprise Linux $releasever - $basearch #baseurl=http://rpms.famillecollet.com/enterprise/$releasever/remi/$basearch/ mirrorlist=http://rpms.famillecollet.com/enterprise/$releasever/remi/mirror enabled=1 priority=10 gpgcheck=1 gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-remi failovermethod=priority [remi-test] name=Les RPM de remi en test pour Enterprise Linux $releasever - $basearch #baseurl=http://rpms.famillecollet.com/enterprise/$releasever/test/$basearch/ mirrorlist=http://rpms.famillecollet.com/enterprise/$releasever/test/mirror enabled=0 gpgcheck=1 gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-remi
Установка MySQL 5
Сначала установите MySQL 5 следующим образом:
|
Затем мы создаем автозапуск для MySQL (так, что бы MySQL запускался автоматически при загрузке системы) и запустить сервер MySQL:
|
Теперь проверьте, что сеть включена. Выполним:
|
[root@server1 ~]# netstat -tap | grep mysql tcp 0 0 *:mysql *:* LISTEN 2479/mysqld [root@server1 ~]#
Если этого не произойдет, отредактируем /etc/my.cnf и закомментируйте опцию пропустить сетей:
|
[...] #skip-networking [...]
и перезапустить MySQL сервер:
|
Запустим:
|
Установим пароль для пользователя root (в противном случае любой желающий cможет получить доступ к MySQL базе данных!):
[root@server1 ~]# mysql_secure_installation
NOTE: RUNNING ALL PARTS OF THIS SCRIPT IS RECOMMENDED FOR ALL MySQL
SERVERS IN PRODUCTION USE! PLEASE READ EACH STEP CAREFULLY!
In order to log into MySQL to secure it, we'll need the current
password for the root user. If you've just installed MySQL, and
you haven't set the root password yet, the password will be blank,
so you should just press enter here.
Enter current password for root (enter for none): - ENTER
OK, successfully used password, moving on...
Setting the root password ensures that nobody can log into the MySQL
root user without the proper authorisation.
Set root password? [Y/n] - ENTER
New password: - Ваш root SQL пароль
Re-enter new password: - Ваш root SQL пароль
Password updated successfully!
Reloading privilege tables..
... Success!
By default, a MySQL installation has an anonymous user, allowing anyone
to log into MySQL without having to have a user account created for
them. This is intended only for testing, and to make the installation
go a bit smoother. You should remove them before moving into a
production environment.
Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] - ENTER
... Success!
Normally, root should only be allowed to connect from 'localhost'. This
ensures that someone cannot guess at the root password from the network.
Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] - ENTER
... Success!
By default, MySQL comes with a database named 'test' that anyone can
access. This is also intended only for testing, and should be removed
before moving into a production environment.
Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] - ENTER
- Dropping test database...
... Success!
- Removing privileges on test database...
... Success!
Reloading the privilege tables will ensure that all changes made so far
will take effect immediately.
Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] - ENTER
... Success!
Cleaning up...
All done! If you've completed all of the above steps, your MySQL
installation should now be secure.
Thanks for using MySQL!
[root@server1 ~]#
Установка Nginx
Nginx доступен в виде пакета для CentOS 6.0 (от EPEL), который мы можем установить следующим образом:
|
Затем мы создаем автозапуск для Nginx и запустим его:
|
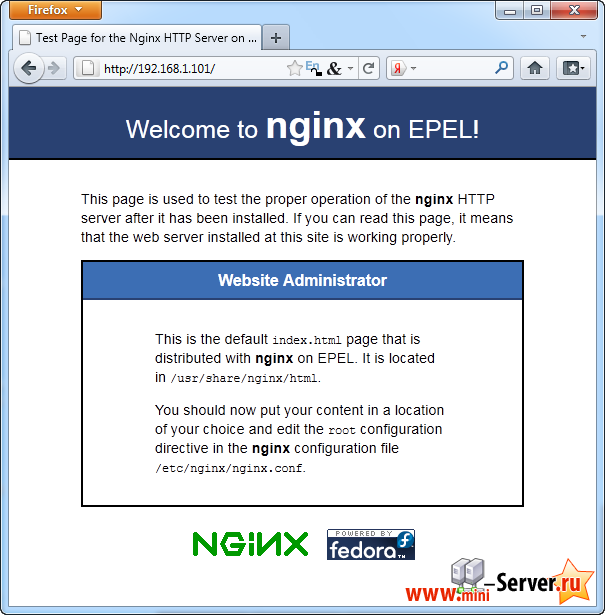
Введите IP-адрес вашего Web сервера или хоста в браузере (например, http://192.168.1.101 ), и Dы увидите пустую страницу (пустая, поскольку /usr/share/nginx/html/index.html пуст). Тем не менее Nginx работает, потому что мы видим пустую страницу):
- Назад
- Вперёд >>


